Generic RESTful API Development
Introduction
In this tutorial we’re going to create a generic restful api, without writing too much back-end java code.
In the end of this tutorial, our controllers will look like this.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/grants")
public class GrantController extends GenericRestController<Grant> { }
and we will be written no sql or hibernate queries. our dao classes will be like:
public interface GrantDao extends BaseDao<Grant> { }
but our Restful services will be available.
Before Starting
You can download the latest source code for this tutorial from my github repository.
You can also view all the changes in the repository by viewing my commits.
Download Initial Project From Spring Initializr
If you want to go through the tutorial yourself, you need to download initial project from Spring Initializr with Web, HSQLDB, JPA dependencies
Here’s how it looks like, in my case.
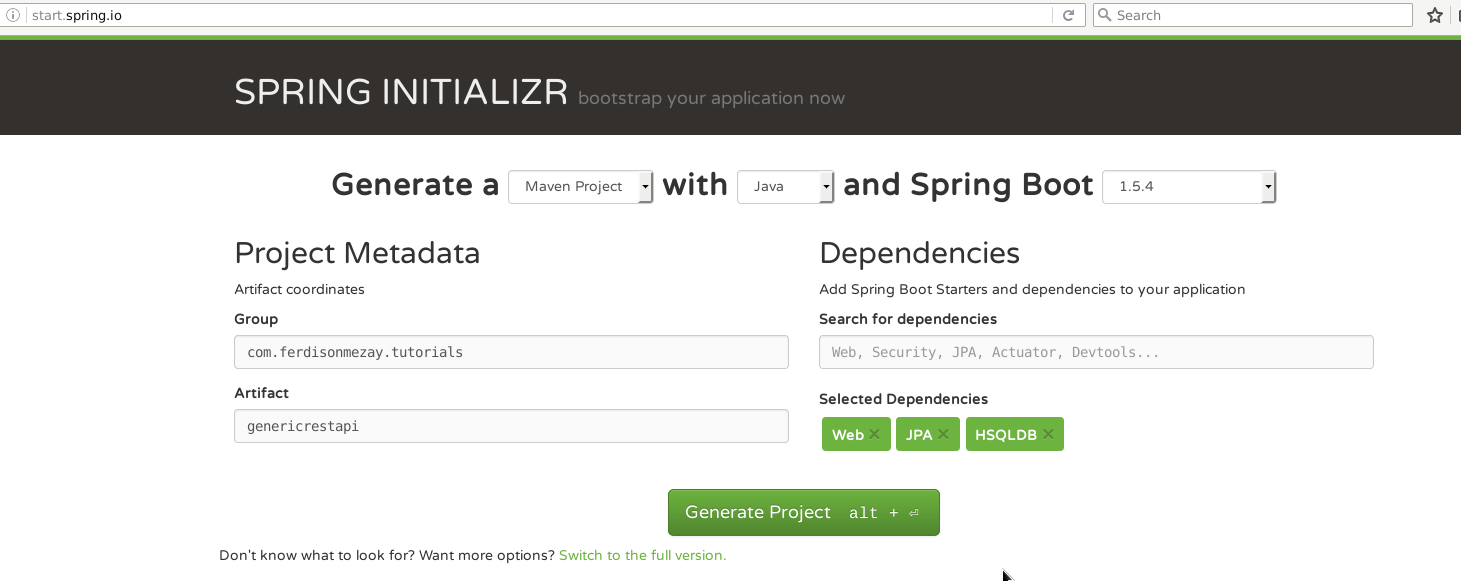
The project you’ve downloaded will be a maven project, you can import the project
to your favorite IDE (mine is Eclipse) and start to make changes.
Create Entity Classes
After you imported the project, we need to create our Entities, so I’ve created
a package com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.model and added three classes
in this package.
-
BaseModel.javawill be super class for all entity classes -
Grant.javais an entity class -
Role.javais an entity class
BaseModel.java is as follows
package com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Basic;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.MappedSuperclass;
@MappedSuperclass
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class BaseModel implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Basic(optional = false)
@Column(name = "id", nullable = false, columnDefinition = "BIGINT")
private long id;
public long getId() { return id; }
public void setId(long id) { this.id = id; }
}
Grant.java is defined as follows:
package com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
@Entity
@Table(name="restapi_grants")
@JsonIgnoreProperties({"hibernateLazyInitializer", "handler"}) // json config
public class Grant extends BaseModel {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4192997147639777673L;
@Column(name="grant_name") private String name;
@Column(name="grant_key") private String grantKey;
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public String getGrantKey() { return grantKey; }
public void setGrantKey(String grantKey) { this.grantKey = grantKey; }
}
Role.java is defined as follows:
package com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
@Entity
@Table(name="restapi_roles")
@JsonIgnoreProperties({"hibernateLazyInitializer", "handler"}) // json config
public class Role extends BaseModel{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1938567246027507296L;
@Column(name="role_name") private String name;
@Column(name="role_key") private String roleKey;
@Column(name="is_active") private boolean isActive;
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public String getRoleKey() { return roleKey; }
public void setRoleKey(String roleKey) { this.roleKey = roleKey; }
public boolean isActive() { return isActive; }
public void setActive(boolean isActive) { this.isActive = isActive; }
}
Create Dao Classes
For database operations we need to create dao classes, for each entity. first
I’ll create com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.dao package and then,
I’m going to create a BaseDao.java superclass which is extended from
JpaRepository.
- BaseDao.java
- GrantDao.java
- RoleDao.java
First we need to create BaseDao.java as follows:
package com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.dao;
import java.io.Serializable;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.model.BaseModel;
public interface BaseDao<T extends BaseModel> extends JpaRepository<T, Serializable> {
}
GrantDao.java is as follows:
package com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.dao;
import com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.model.Grant;
public interface GrantDao extends BaseDao<Grant> {
}
RoleDao.java is as follows:
package com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.dao;
import com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.model.Role;
public interface RoleDao extends BaseDao<Role> {
}
Create Controllers
When creating controllers, we will use the same method that we’ve used in creating dao classes. There will be one superclass that will be extended by each controller. We will implement Restful services only once in the superclass, and use them in each controller.
- GenericRestController.java
- GrantController.java
- RoleController.java
GenericRestController.java is as follows:
package com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.dao.BaseDao;
import com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.model.BaseModel;
public class GenericRestController<T extends BaseModel> {
@Autowired
private BaseDao<T> dao;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<T> list() { return dao.findAll(); }
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public T create(@RequestBody T entity) { return dao.save(entity); }
@RequestMapping(value = "{id}", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public T update(@PathVariable(value = "id") long id, @RequestBody T entity) { return dao.save(entity); }
@RequestMapping(value = "{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public void delete(@PathVariable(value = "id") long id) { dao.delete(id); }
@RequestMapping(value = "{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public T get(@PathVariable(value = "id") long id) { return dao.getOne(id); }
}
GrantController.java is as follows:
package com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.model.Grant;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/grants")
public class GrantController extends GenericRestController<Grant> {
}
RoleController.java is as follows:
package com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.model.Role;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/roles")
public class GrantController extends GenericRestController<Role> {
}
After you created the controllers, now you can test your restful services by
running GenericrestapiApplication.java class as Run As –> Java Application
or by running
mvn spring-boot:run
command on terminal.
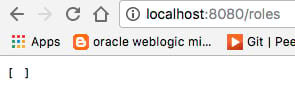
after the appication run, you can go to http://localhost:8080/roles
if everything is ok, you must see Square brackets which means roles list is empty, as shown in screenshot below.
Swagger Integration
Finally I’m going to create swagger integration to test and document our RESTful services.
We need to add swagger dependencies to our pom.xml file.
<dependencies>
...
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0</version>
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>
then I’m going to create a SwaggerConfig.java configuration file, in
com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.configuration package.
SwaggerConfig.java file will be as follows:
package com.ferdisonmezay.tutorials.genericrestapi.configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket api() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any())
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build()
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.useDefaultResponseMessages(false);
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
ApiInfoBuilder apiInfoBuilder = new ApiInfoBuilder();
apiInfoBuilder.title("Generic REST API");
apiInfoBuilder.description("Simple REST API Generation");
apiInfoBuilder.version("0.0.1-SNAPSHOT");
apiInfoBuilder.contact(new Contact("Ferdi Sonmezay", "https://ferdisonmezay.com", "hi@ferdisonmezay.com"));
apiInfoBuilder.license("GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE, Version 3");
apiInfoBuilder.licenseUrl("https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html");
return apiInfoBuilder.build();
}
}
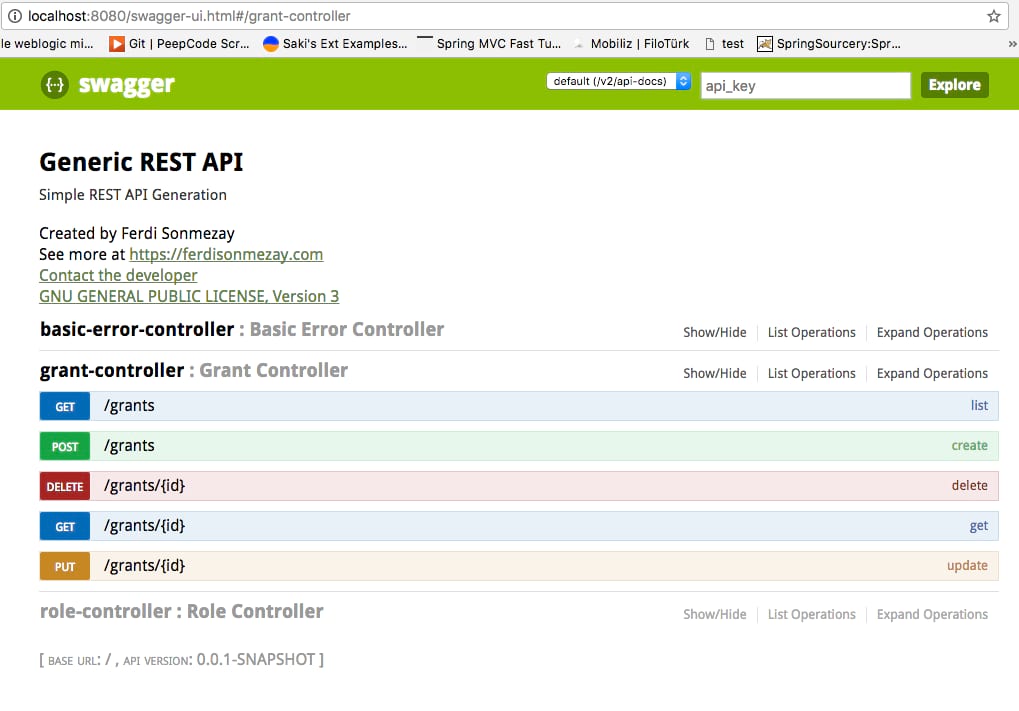
when you run the application, you must be able to see swagger-ui page. From swagger ui, you can test all the rest services we’ve defined.
Summary
Hope this tutorial helps you make faster restful service development.